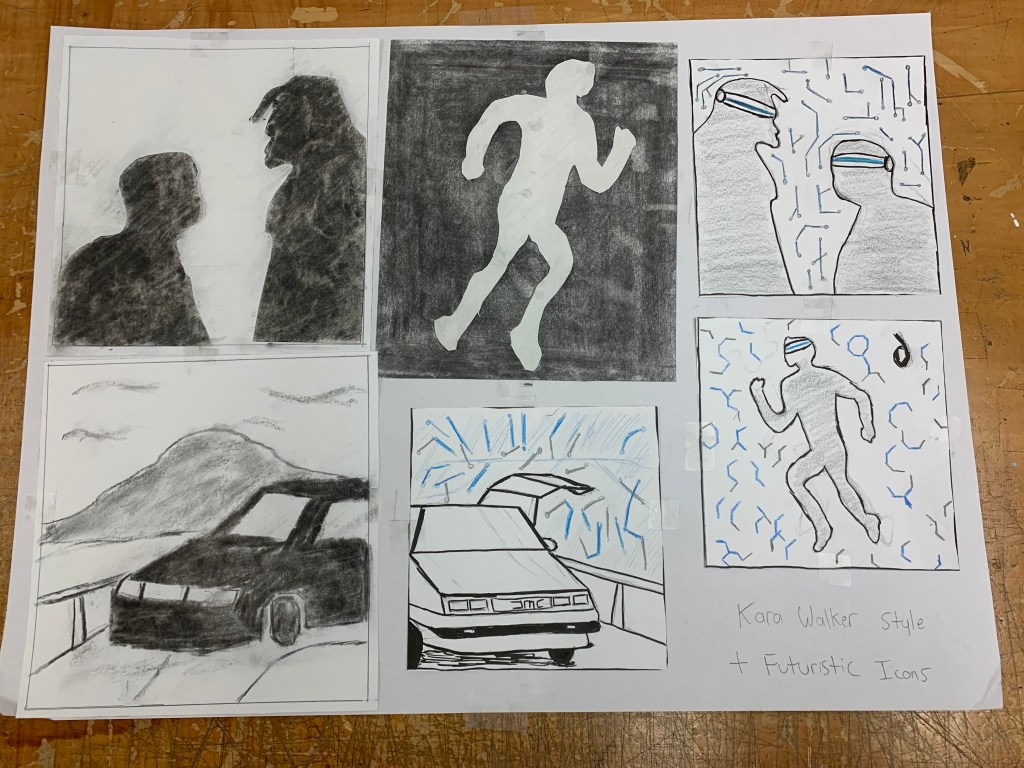
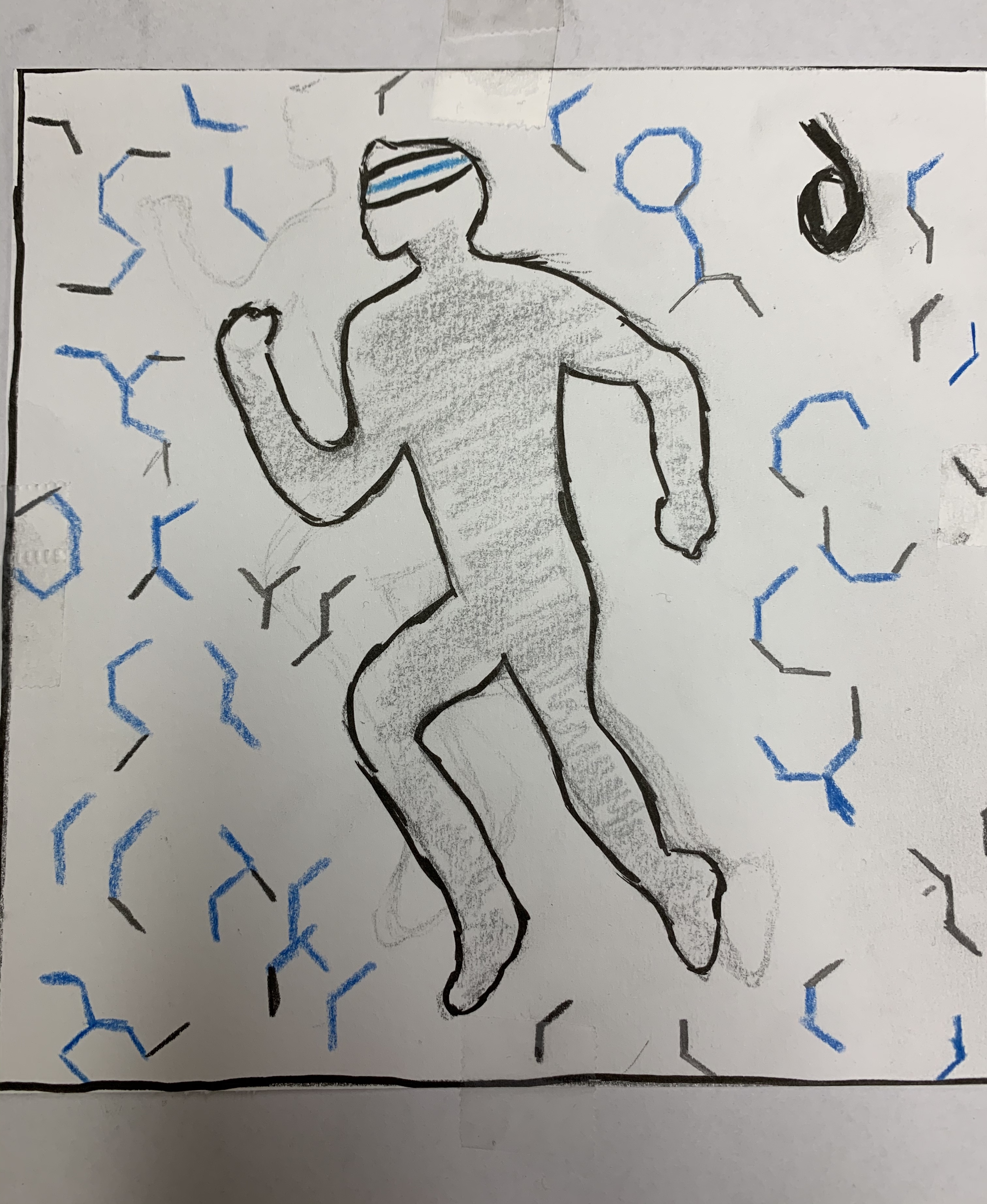
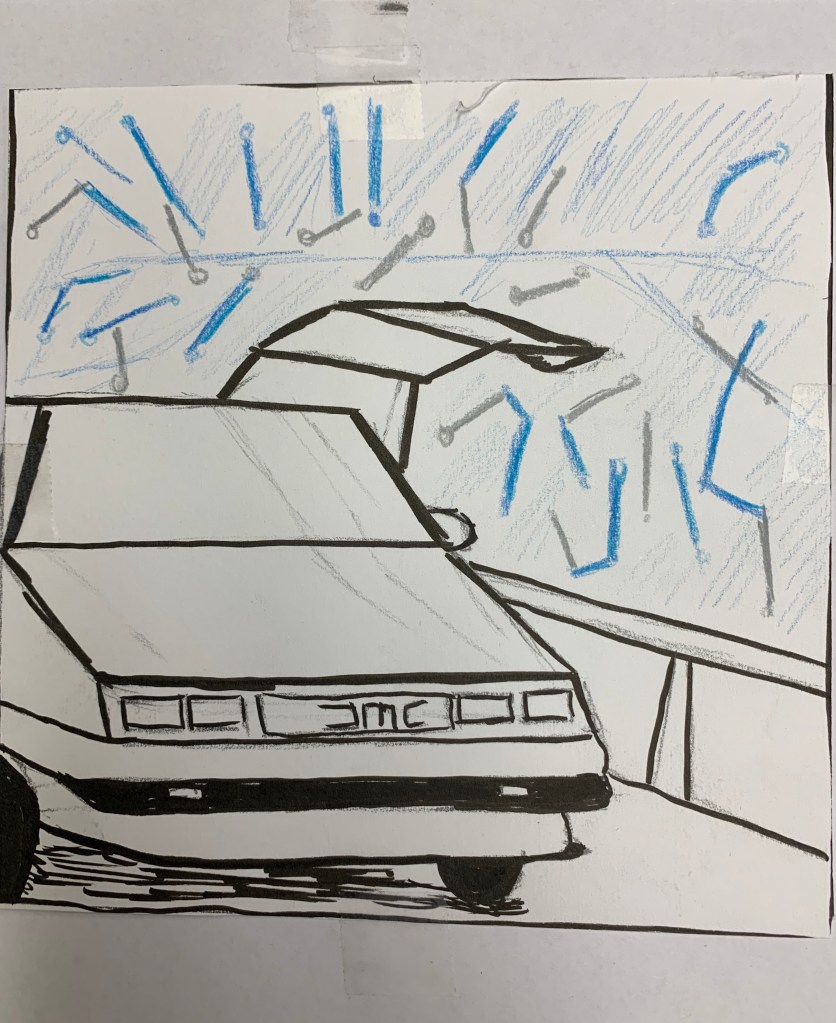
Intro
- Shared connection with Visual and Music Rhythm
- Kinesthetic empathy – a visual experience that strikes a sense in our mind
- Different designs such as curves, repetition, when looked at can a create sound in the head similar to real sounds
- Rhythm is commonly related to sound, but visually it can be a sense of movement and repetition
Rhythm and Motion
- legato – meaning
- Shapes and arrangement is key besides colors and lines
- Constant movement can give a sense of a fast state and use of transitions can be applied
- Manipulating stokes to create irregular movement can also be used to give off a unique rhythm
Alternating Rhythm
- When there is a sequence and order to the pattern to know what is expected
- repeating lines and colors with different and alternating directions help in getting attention
Progressive Rhythm
- progression of repetition with regular changes
- Inherent Rhythm – obvious repetition with subtle small progression
Polyrhythmic Structure
- complex rhythm
- use of several different rhythm patterns